3. Climate and climate change
The greenhouse effect (2/4)
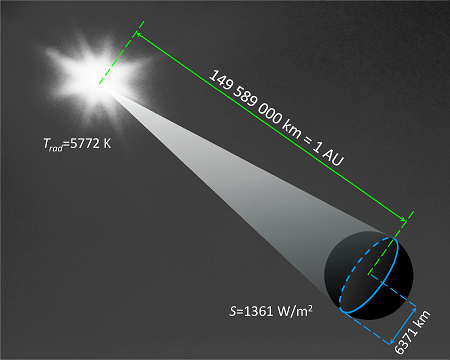
How much solar radiation does the Earth absorb?
When viewed from the sun, the Earth appears like an illuminated disk. With the radius of the Earth RE = 6371 km, the area of this disc is:
A completely black Earth would absorb all the incident solar radiation. The absorbed power would be:
The Earth as a blue planet only absorbs a part the incident radiation. The albedo describes the proportion of reflected radiation back out into space. The albedo of the Earth has a value of A = 0.3. This means, 70% of the incident radiation is absorbed:
How does the Earth radiate into space?
At any given moment, only half of the Earth's surface is irradiated by the sun, but the Earth itself radiates from its entire surface into space. The amount of radiation from any part of the surface depends on many things, such as latitude and the seasons. This simple model removes the need for those specific details by using the mean temperature of the entire surface of the earth.
Like the sun, the emission of the Earth's surface is defined as the product of the surface area with the Stefan-Boltzmann law,
where Trad,E is the mean radiative temperature of the Earth's surface. Now the task is to find this temperature.