تعانى مدينة مكسيكو سيتى من اكثر مشاكل تلوث الهواء سوءً على مستوى العالم. تقع المدينة على قمة سهل مرتفع يبلغ ارتفاعه 2.200 متراً، وهى محاطة من ثلاثة جوانب بجبال وبراكين قممها مغطاه بالجليد.
التحليق فوق مكسيكو سيتى
For the display of this element you need a Flash-Player from Version 8 on.
إن المصادر الرئيسية لملوثات الهواء فى الحوض الذى يضم المنطقة العمرانية لمدينة مكسيكو سيتى تشمل العادم الناتج من 3.5 مليون مركبة تعمل غالباً ببنزين غير رصاصى أو ديزل فوسفورى. آلاف الصناعات تمثل خمس الصناعات المكسيكية توجد فى العاصمة بإمكانات قديمة جزئياً، ويضاف إلى المشكلة الغبار المعدنى. إنوادى البحيرة القديم الذى تقع فيه مدينة مكسيكو سيتى قد تم تجفيفه فى القرن السادس عشر وأصبح مصدراً رئيسياً للغبار والعواصف الترابية , الترابية التى تسمى Tolvaneros.
وفى كل يوم تنبعث فى الهواء 1200 طن من الملوثات السامة وعلى ارتفاعات أكثر من 2.200 متر فان تأثير الأشعة فوق البنفسجية تكون أعلى، بينما تقل كمية الأكسجين بنسبة 15%. ولذلك فان عملية الاحتراق بالسيارات والصناعة قد أثرت كثيراً. ان الإرتفاع العالى وشدة ضوء الشمس هى العوامل المؤثرة على تكوين الأوزون (Bauer et al. 2005, Claaßen 2008, NASA Visible Earth, Yip, Madl 2000).
ضباب فوق مكسيكو سيتى
ضباب فوق مكسيكو سيتى
المصدر: NASA Visible Earth
معلومات عن الصور الفضائية ↓↑
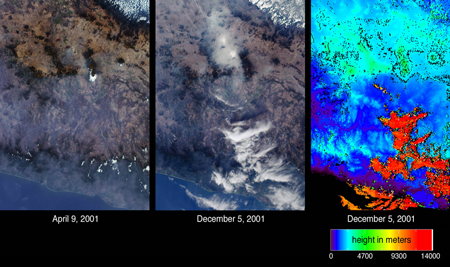
Atmospheric particulates (aerosols) and differences in their amounts on two days are indicated by the images of central Mexico from the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR). The images on the left and in the center are natural color views acquired by MISR´s camera on April 9 and December 5, 2001, respectively. Mexico City can be identified in the center image by the large area of haze accumulation above the image center. Two small brighter patches within the hazy area indicate low fog. In the left-hand image, the city basin appears significantly clearer, but some haze remains apparent across the Sierra Madre mountains in the lower portion of the images. On the right is an elevation field corresponding to the December 5th view. This depiction reveals the clouds at the lower right to be at very high altitudes, in contrast to the low-lying haze and fog near Mexico City. When a location is not covered by clouds, digital terrain elevation data is displayed instead. High clouds appear as the orange and red areas, and mountainous areas appear light blue and green (NASA Visible Earth).
المشاكل الصحية
لا زال عدد الناس الذين يعانون من أمراض الجهاز التنفسى و التهابات العيون يتزايد نتيجة لمشاكل تلوث الهواء فى مدينة ميكسيكو سيتى (Bauer et al. 2005).
الهدم البيئى فى مكسيكو سيتى ↓↑
In the case of the Mexico City Metropolitan Area the major health impacts of air pollution originate from three major pollutants: suspended particulate matter, ozone (a secondary pollutant) and lead. It was estimated that some 11.2 million work-days would be saved each year by reducing pollution. 6 400 people a year are dying prematurely with an average of 12.5 years of life being lost because of pollution emissions which exceed legislative standards.
In regard to ozone pollution there are a number of other serious health problems including asthma attacks, eye irritation, mild cough, sore throat, headache and chest discomfort.
Lead is a particularly dangerous air pollutant. Nearly 95 percent of gasoline in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area, still contains lead. Relating to children a reduction in IQ is a result of lead poisoning. In adults, high levels of lead result in a number of health problems including high blood pressure and myocardial infarctions.
The water supply is another major environmental problem in Mexico City. Since the middle of the last century, underground water has been used, significant subsidence damage has been caused in the city itself with the ground level falling by eight metres or more in the historical part of the city.
The costs of these problems go into hundreds of millions of dollars (Margulis 1992).
المهام:
1- أوصف الموقع الطبوغرافى والوضع المناخى لمدينة مكسيكو سيتى بالاستعانة بالفلم والتقرير.
2- أشرح الصور الفضاء وتوضيح الضباب. ما معنى مناطق الضوء الأزرق هنا؟.
3- إشرح المشاكل البيئية، مع الرجوع إلى الموقع، المناخ، ونفايات الموارد.

