Mexico City (3/3)
In winter, air quality can worsen significantly when thermal inversions keep polluted air masses close to the surface. In these spells of weather the polluted air cannot escape and fresh air supply is only limited. This causes a brown pall of smog over the city on 200 days per year with an increasing concentration of pollutants in near-ground air layers.
Winds tend to blow across the city from the northeast, where a slight opening in the mountains allows moisture and winds from the Gulf of Mexico to enter the basin. These winds blow pollution from the region of heaviest industrial development towards downtown and the residential areas southwest of the city which are pressed against the southern mountain chain (Bauer et al. 2005, Claaßen 2008, NASA Visible Earth, Yip, Madl 2000).
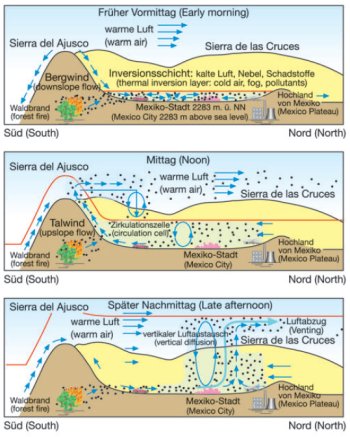
Source: Appleby 2007
Further environmental problems in Mexico City
The mega city of Mexico City also faces a number of other serious environmental problems such as waste, water and sewage disposal. The natural precipitation of 700 mm is not sufficient to supply water to all inhabitants. Groundwater lowering and an expansion of build-up areas cause higher transpiration and faster above-ground runoff of heavy rainfalls in the summer. The water flows over 100 km in pipes to the city, but the insufficient water distribution causes the need for one quarter of the inhabitants to be supplied by road tankers. The water quality is often poor, causing diseases. The old canalization is completely overloaded, most of the sewage disappears untreated in canals and rivers (Bauer et al. 2005).
Can you imagine with the images below, that the blue sky and the surrounding mountains are rarely visible from the urban center because of the local air pollution?

Mexico City under a pall of smog.
Photo: Carlos Oscar Ruiz |

Haze over Mexico City.
Photo: Carlos Oscar Ruiz Photo: Carlos Oscar Ruiz |

Blue sky over Mexico City?
Photo: Carlos Oscar Ruiz |

Mexico City at night.
Photo: Carlos Oscar Ruiz |
Transportation improvement program
Mexico City has made important efforts to reduce air pollution. Any strategy aiming to reduce or control atmospheric pollution has to include a transportation improvement program because transportation has proved to be a major pollution source within the Mexico City Metropolitan Area.
Following measures have been undertaken:
- one day stop program for private cars called "HOY NO CIRCULA"
- biannual test for private cars to enforce engine maintenance standards
- expansion of public transport (metro system), incentives for car owners to use public transport
- change of fuels, reduction of lead and sulphur in fuels, compulsory implementation of catalytic converters
- shutdown of factories violating environmental restrictions
- monitoring of air quality
Because of private interests, corruption, indulgence, ineptitude and decisions more political than scientific, quick improvements have obstructed the fight against air pollution (Claaßen 2008, Yip, Madl 2000).
Tasks: 1. Describe the conditions created by the atmospheric inversion over Mexico City.
2. What are the causes of this atmospheric phenomenon?
3. Which of the transportation measures do you think will be most effective, and why?
