Soil Line
Soil has a particular spectral signature that differenciates it from other land cover types. In the visible and near infrared region, reflectance increases in proportion to the wavelength increase. However, the rate of increase is affected by many factors. Soil texture and structure establish whether the soil reflects energy as a diffuse or lambertian reflector. Soil moisture and organic matter increase soil absorbency and result in overall lower soil reflectance.
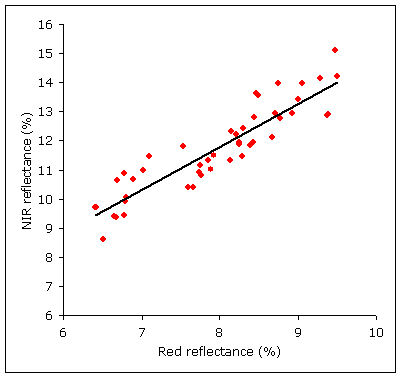
However, the relationship between red and near-infrared reflectance remains relatively constant for a specific soil type with particular characteristics. If we were to collect many spectral measurements of the same soil, under different moisture content conditions, and then plot the red against the near infrared reflectance for each measurement, we would get something like the following figure:
Because the reflectance between red and near infrared fluctuate proportionally, when the moisture content changes, those two values are said to be correlated and have a linear relationship. This means that whenever one changes, the other changes according to the relationship that binds the two. The line that describes that relationship is known as the soil line, which is unique for each soil.