5. Urban Planning
Urban land cover changes
How simple is it to classify urban land cover?
One of the primary obstacles to urban land cover classification is the diversity and spectral heterogeneity of urban reflectance. Compared to other land cover types, urban reflectance is extremely variable at a variety of spatial scales. Urban areas provide examples of spectrally diverse, scale-dependent thematic classes containing large numbers of pixels that are spectrally indistinguishable from other land cover classes. The diversity of land cover types and scales in the urban mosaic therefore results in high rates of misclassification between urban and other land cover classes.
The most accurate methods
Spectral Mixture Analysis (SMA) provides a physical basis on which to quantify the spectral characteristics of diverse mosaics of land covers and distinguish spectrally heterogeneous urban areas from more spectrally homogeneous non-urban land covers. SMA is based on the observation that, in many situations, radiances from surfaces with different endmember reflectances mix linearly in proportion to area within the instantaneous field of view (IFOV).
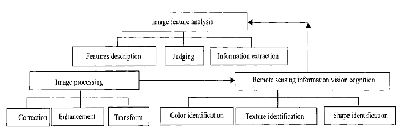
Extraction model based on the multifeatures of object land covers. The classification and extraction model based on the multi-features of urban land-use is set up based on human vision and sensory principles, by integrating mathematical statistics and artificial intelligence, in the support of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Expert Systems (ES), and by fusing different kinds of image features, as well as imitating geography experts cognition and knowledge of images.
The method based on the multi-features of the objects has a strong ability to counteract noise, and the urban land-use plot has integrity. Based on intersected image, the object has more semantic information. So the classification method based on the multifeatures is more scientific and reasonable.
The model includes three sub-models:
- image processing (offers a clear and abundant image for remote sensing information vision cognition)
- remote sensing information vision cognition(simulates the interpretation of the experts, and identifies the shape, texture and color of the object)
- analysis of image characteristics (links the objects with their features, and obtains an extraction result through decision-making and judgment)